The ELISA plate is a plate used for enzyme-linked immunosorbent experiments on a microplate reader. The commonly used one is 96 wells, which are mainly designed to cooperate with the microplate reader. There are also 48 wells, but they are not commonly used. In the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, antigens, antibodies, and other biomolecules are adsorbed to the surface of the ELISA plate through various mechanisms, and then react with the tested sample and the ELISA-labeled antigen or antibody according to different steps, and are detected by the ELISA reader.
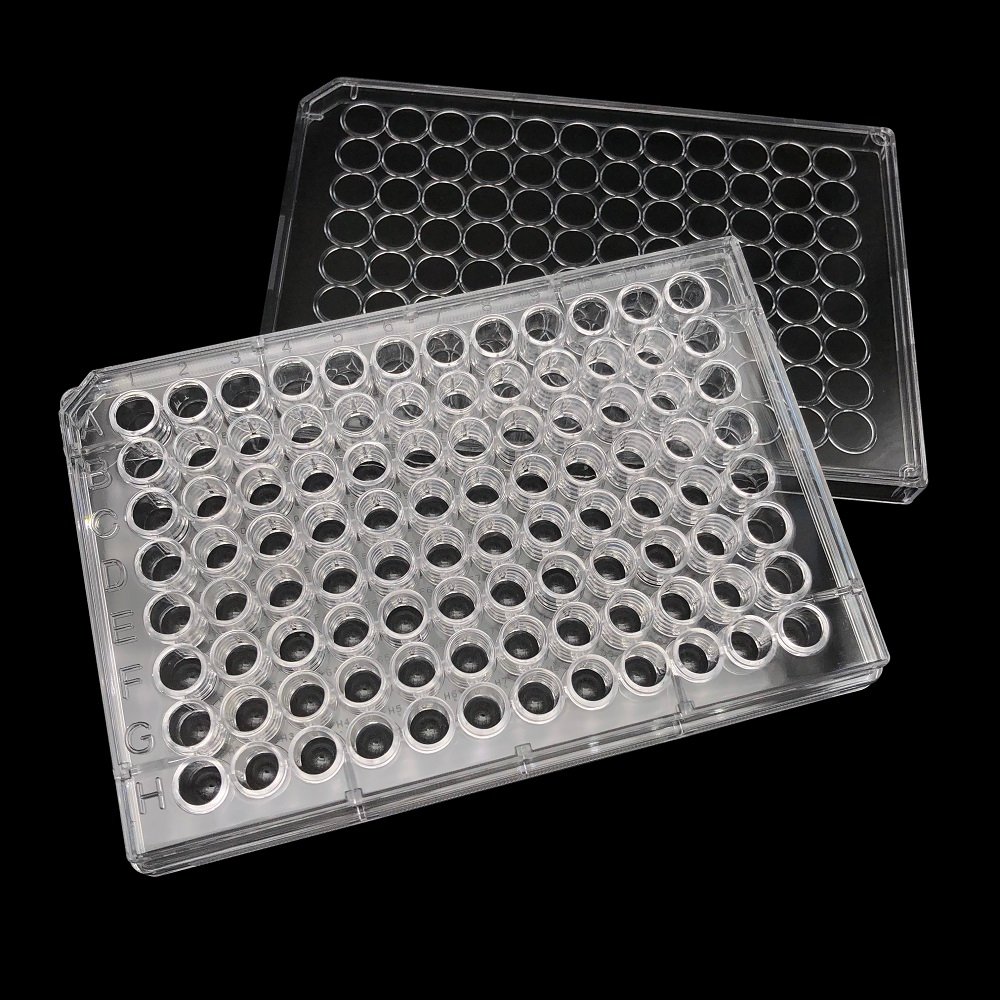

The culture plate is used to culture cells or bacteria, and there are 6 wells, 12 wells, 24 wells, 48 wells, and 96 wells. Similar to the transparent microplate, the use is very different. Add an appropriate amount of culture medium to the wells of the culture plate, and then carry out cell culture in a suitable environment. General culture plates are flat-bottomed, suitable for suspension culture of cells and tissues, and there are also U-bottom and V-bottom. After surface modification treatment, it can have cell adherent culture and growth properties.
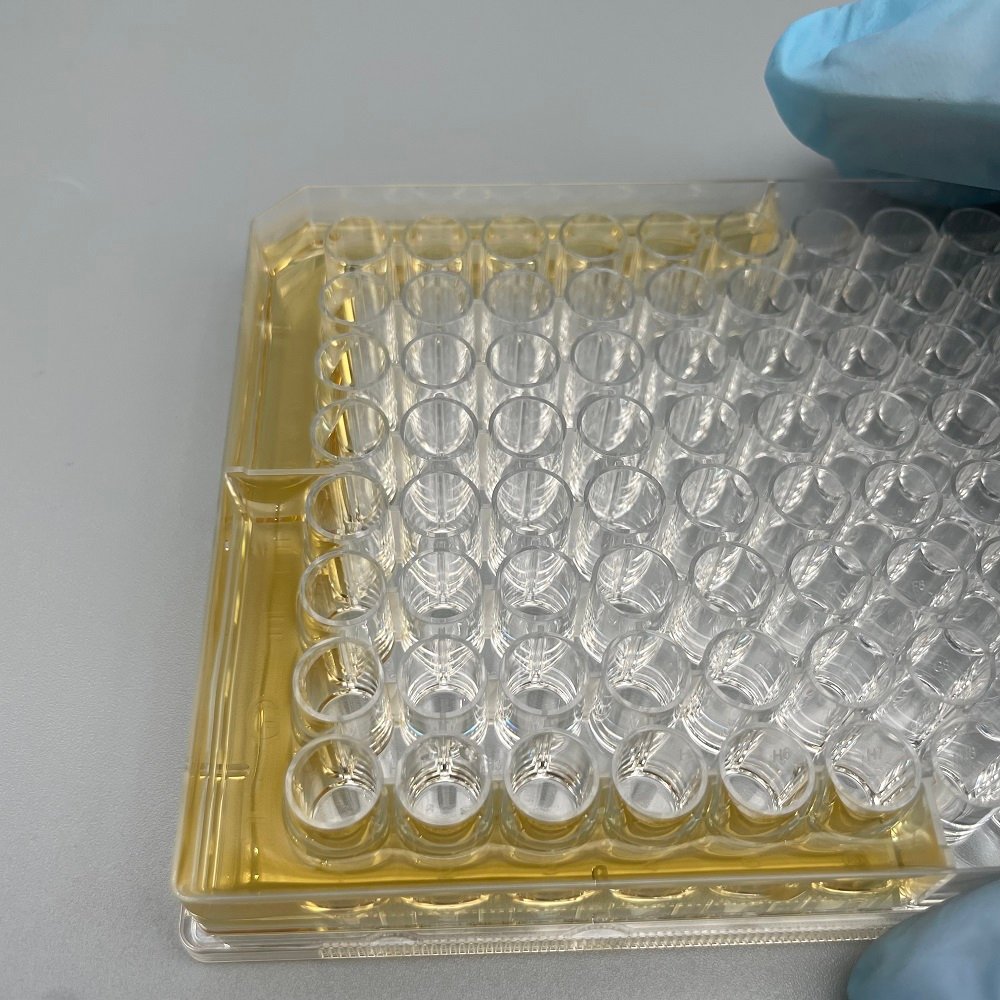
The two materials are very different. The microplate material is polystyrene, which can adsorb proteins. However, the cell culture plate does not adsorb proteins, so it must not be confusing, otherwise, there will be no results when doing ELISA. The precision and specificity of ELISA plates are higher. The ELISA plate is generally more expensive than the cell culture plate. The cell plate is mainly used for cell culture and can also be used to measure protein concentration; the ELISA plate includes the coating plate and the reaction plate and generally does not need to be used for cell culture. After protein detection, higher requirements and specific enzyme labeling working solutions are required.





